Control Of Microbes Using Chemicals
Like many physical methods chemical agents can be either biostatic
or biocidal. In many case the same chemical can be either
of these depending on the concentration
Biostatic treatment inhibits further growth of organism with
out killing them.
This ia an advantage for cleaning hands and body surface were you don't
want to kill the beneficial commensalistic bacteria. If your skin as sterilized
it would easily get infected by pathogens once exposed to the environment.
Commensals on the skin, in body cavities and the intestine inhibit pathogen
growth by competition for resources and via ammensalistic interactions.
There are often small numbers of pathogens living in or on our bodies under
control of commensals. If the commensals are killed the pathogens can grow
with out inhibition. This is called autoinfection because the infection
is already present on our bodies. e.g. pneumonia, diphtheria and thrush
and other fungal infections.
Once biostatic conditions are established they can be maintained
and prevent bacteria growing even if they enter at a later time.
Biocidal treatment has its place when no growth is needed. Such
as when preparing an area for surgery or sterilizing medical materials.
Once used the biocidal treatment may not have a continuing effect and sterilized
material must be kept in sealed containers
The effect of a chemical treatment is dependent on the same parameters
as physical controls:
| Initial number organisms |
| The time of exposure |
| Intensity of treatment |
| Resistance of the organism |
| Chemical being used |
Most of these chemical agents will react with organic mater so that if
material to be disinfected is soiled the agents may be exhausted by reaction
with extraneous filth before it has a chance to react with the microbes.
Disinfection
is not a substitute for proper cleaning. Surfaces must be washed thoroughly
before chemical sanitation.
Classification of Chemical Agents
|
Disinfectants
|
|
Sanitizes
|
|
Sanitizes
|
|
Antibiotics
|
Disinfectants are chemicals that kills or inhibits organisms
but is not safe to use in or on living tissue and must be restricted to
use on inanimate objects
Antiseptics are chemicals that kills or inhibits organisms
and is safe to use in or on skin or mucus membranes but may not be
safe to take internally
Antibiotics are are chemicals that kills or inhibits organisms
are safe to used internally. The ideal antibiotic will kill microbes and
have ne effect on the patient. However the ideal is not always achieved
and some antibiotics have serious side effects on the patient.
Sanitizes are used to clean surfaces and equipment that is to
be used for preparation of food drugs or cosmetics. Theses chemicals must
be safe in case of residues remain
on the surface and enter the food or other products.
Chemicals act as Antiseptics
and/or Disinfectants by reacting as Oxidising agents,
protein denaturants ,as surfactants
disruping fatty membranes or reacting with nucleic acids.
Oxidizing Agents
Chemicals that kill by oxidizing microbial material such as lipids, proteins
and nucleic acids
These chemicals often react via production of very reactive singlet
oxygen(  ).
).
e.g. Chlorine is added to water
as a gas and levels of 2 ppm. of available chlorine is needed to effectively
kill microbes. When chlorine is added to water some quantity must be added
before any available chlorine is detected. This is called the break point.
Break point is when the organic mater in the water has been saturated with
chlorine from then on added chlorine causes a rise in available chlorine.
Chlorine reacts in water to give hypochlorous acid (HOCl) which decomposes
to yield singlet oxygen:
Cl2
+ H2O --> HOCl + HCl
HOCl
--> 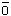 + HCl
+ HCl
Chlorine can be added as a sodium
salt of Hypochlorate (NaClO). This white powder is used when chlorinated
swimming pools and wine bottles when home brewing etc.
Household bleach is usually a solution
of sodium hypochlorite. excellent disinfectants can be prepared at home
using a 1:1000 dilution of bleach (or one cap full in a bucket of water).
Diluted bleach is often used as a sanitizes in kitchens.
Protein Precipiants:
Iodine reacts
by combining with the aromatic amino acids in proteins
A crystal of solid iodine can be added as such to water as a sanitiser.
This is done with water purifier kits supplied to people on outdoor activities
Solutions of iodine were one of the first used as antiseptics in The
USA civil war to "cold cauterise wonds" before that cuts and wounds were
treated by cauterising with red hot iron.
Heavy metals denature protein by
reacting with SH groups in amino acid residues
Alcohols denature Protein by coagulation in the presence of water. Without
water alcohil can preserve the microbe instead of killing it
Formaldehyde ans ethylene oxide denature protiens by adding acyl groups
( R-) to the free NH2 on amino acids (acylation)
Membrane Disruption:
Detergents can kill microbes by
disrupting their phopholipd membranes. Gran -ve bacteria and enveloped
viruses such as HIV are more effected than Gram +ve bacteria and naked
viruses.
cf. nanoxinol on condoms
Reaction with DNA
Dyes can react with nucleic acids
and were uses as the first "magic bullets" in treating diease
They have been replaced by modern antibiotics but as microbes become
resistant dyes may be used again one day.
Table of Actntiseptics and Disinfectants and
How They Act